爱德思(Edexcel)物理U5复习提纲&简答题全整理:热力学、辐射、振动和宇宙学
爱德思(Edexcel)物理U5复习提纲&简答题全整理:热力学、辐射、振动和宇宙学
Carkree爱德思物理U5的难度是小于U4的,但可惜我没时间刷太多题。本文就记录一下简答题的总结吧
第一部分 主要公式以及复习提纲
一、简谐运动
$T = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{m}{k}} = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{L}{g}},$
$\omega = \sqrt{\frac{g}{L}},$
$v = \omega\sqrt{A^2 - x^2},$
$x = A\cos\omega t,$
$v = -A\omega\sin\omega t,$
$a = -A\omega^2\cos\omega t$
这个还是比较好记忆的,并且公式表都有写。尤其是x,v和a的关系,只需要记住是求导和积分的关系
二、热力学
Internal energy:内能是下面两个部分的和
- potential energy:持续吸热,但温度不变,即内能增加
- kinetic energy:持续吸热,温度升高,即动能增加
Specific heat capacity 比热容
- $C = \frac{Q}{m \Delta t}$ (单位:$J/kg \cdot ^\circ C$)。$C$ 取决于物体和它的状态
- Definition: Energy absorb/ dissipate per unit mass per unit Celsius
Specific latent heat (适用于温度不变/势能增加)
- $L = \frac{Q}{m}$ (单位:$J/kg$)。$L$ 取决于不同的状态,状态不同$L$不同
- Definition: Energy absorb/ dissipate per unit mass
理想气体:
$PV = nRT= NkT$动能和温度的关系:
$ E_k = \frac{3}{2}kT $
三、Gravitational field
Definition:A region where force will act on the object which has mass.
Gravitational force:
$$F = G\frac{m_1m_2}{r^2}$$Gravitational filed strength
$$g = \frac{GM}{r^2}$$Gravitational potential energy:
$$GPE = -\frac{GMm}{r}$$
四、核
Binding Energy:Minimum energy needed to pull nucleus apart into seperate nucleons.
- Binding energy越大越稳定
Fission 核裂变:一变多,粒子质量相差不大
Fusion 核聚变:多变一无论是核聚变还是核裂变,都属于自发反应,都都释放能量,且每个核子的平均结合能都是从小到大的过程。
半衰期(half life),活跃度(activity)和衰变常数(decay constant)
- 假设现在有$N$个粒子
- 它的decay constant是$\lambda$,这反映了衰变的快慢
- 当前的粒子数量可以用公式来表示:$$N = N_0 · e^{-\lambda t}$$
- 它的活跃度用$A$来表示:$$A = \frac{dN}{dt} = \lambda N$$
所以可以得到,$$A = \lambda N_0·e^{-\lambda t}$$
所以,$$A = A_0·e^{-\lambda t}$$ - 进而,我们可以得出它的半衰期公式(半衰期是放射性核素衰变一半所需的时间)
$$ t_{\frac{1}{2}} = \frac{ln2}{\lambda}$$
五、宇宙
- Intensity:
$$ I = \frac{P}{A} $$- $I$作Intensity
- $P$作Luminosity,即物体释放的中power
- $A$作辐射源与所在的面的球体的面积,$A = 4\pi d^2$
- Standard candle:一个测量luminosity的方法
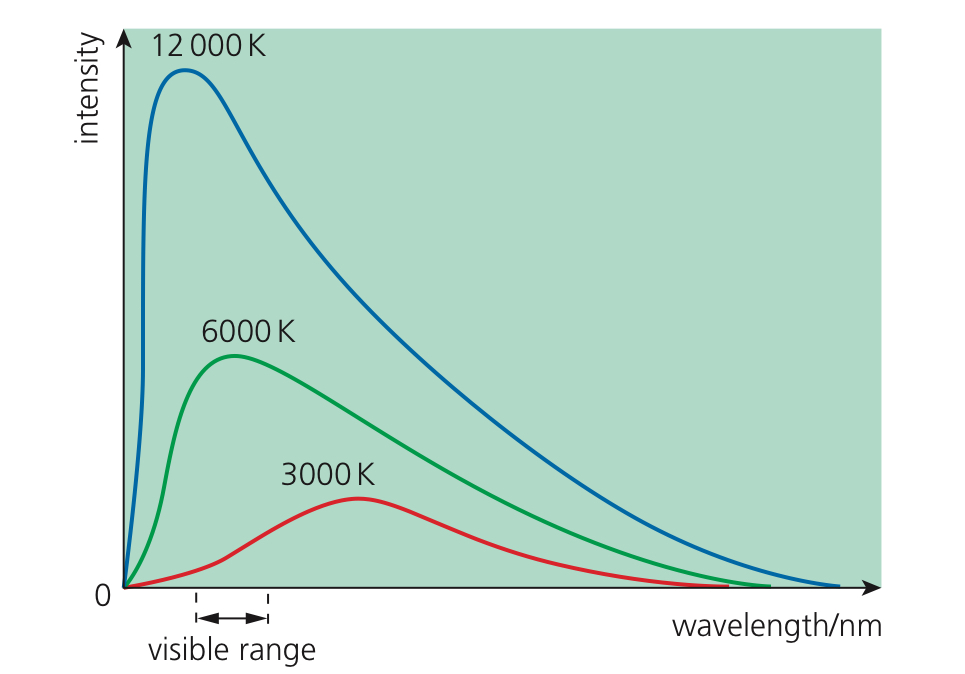
- Steller radii:温度越高,最大intensity的波长越短
- Wien’s displacement law:
$ \lambda_{max} = \frac{b}{T}$
- $b$是constant
- Stefen-boltzman Law:
$ L = 4 \pi \sigma r^2 T^4$ - Red shift/Blue shift和Doppler Shift:

- 红光是波长最长的光。上图中间部位为visible light。
- 当波源朝向观察者运动时,波长会减小,则称之为蓝移
当波源原理观察者运动时,波长会增加,则称之为红移
- Hubble’s Law:
- 两个星系互相以$v$的速度远离,相距$x$,则可计算宇宙的年龄$T$:$$T = \frac{x}{v}$$
- 画一个v-d图,图的斜率则为$H_0$:$$T = \frac{1}{H_0}$$
- $$z = \frac{\Delta f}{f} = \frac{\Delta \lambda}{\lambda} = \frac{v}{c}$$
第二部分 简答题
括号内特别标注的是考试年份
一、标准火烛、平行视差和距离
为什么标准火烛可以测量距离(2016.1)
- Standard candle has a known luminosity
- Radiation flux of standard candle is measured from the Earth
- Use inverse square to calculate the distance
- $F = \frac{L}{4\pi d^2}$
为什么一些标准火烛只能用来测量离得近的星系(2016.1)
Radiation flux is too small to measure
如何用平行视差法测量距离
- Find angular displacement of the star from two positions as Earth moves around the Sun over a 6 month period
- Measurements are made against the background of more distant stars.
- Radius of the Earth’s orbit about the Sun must be known to calculate the distance to the star
- ,using trigonometry
对于特别远的行星,如何测量距离(2016.1)
- We need to know the luminosity
- We need to know the temperature
- Calculate $r$ by using $L = 4\pi \sigma r^{2} T^{4}$
解释哈勃是如何测量星体的速度的,并解释为什么这支持了宇宙膨胀的理论(2016.1)
- Doppler shift formula used to calculate velocities: $z = \frac{\Delta \lambda}{\lambda} = \frac{v}{c}$
- Galaxies were moving away from the Earth。(星系在远离地球)
- $v = H_{0}d$ The further away the galaxy the faster it was moving (星系离得越远,移动的速度越快)
- Therefore all galaxies are moving away from each other (所以所有的星系都在互相远离对方)
为什么标准火烛周围的灰尘会使得得出一个比实际火烛距离地球的距离更大的数值
- 强度–>距离
- A layer of dust around the candle would reduce the intensity.
- Intensity obeys $I = \frac{L}{4\pi d^{2}}$.
- A smaller value of intensity would lead to larger distance, so claim is valid.
二、核聚变与衰变
核聚变发生的条件
- 高温–>高动能–>克服排斥力–>离得更近,大引力–>高密度–>高撞击频率
- Very high temperature in the core
- Nuclei have a high KE
- Sufficient to overcome electrostatic repulsion
- Allow nuclei to get close enough to fusion
- Gravitational force produce a very high density in the core
- So there is a high collision rate.
核聚变和核裂变的定义
- 核聚变:The joining of two smaller nuclei to form a larger nucleus and to release energy
- 核裂变:The splitting of a large nucleus to produce smaller nuclei, fast moving neutrons and energy.
解释什么叫decay randomly(2016.5,2014)
- We cannot know which will decay next
解释什么叫decay spontaneously(2014)
- We cannot influence when a nucleus will decay
Half life的定义
The time taken for half of the radioactive nuclei to decay
为什么在某物质的衰变中,释放的beta粒子的能量会损失?
- KE is given to three particles in the decay
- The energy split between the beta-particle and neutrino is random.
为什么要对count rate进行修正(2016.5)
- The background radiation will increase the recorded count rate
为什么要把核聚变换成核裂变(2014)
- Fission create more radioactive waste, radioactive products produced in fission present significant storage problems
- Fuel of fission is limited resource, fuel of fusion is unlimited.
- The energy released by fusion is greater than the
energy released by fission
解释为什么更多的能量给了alpha particle(2014)
- Alpha particle have small mass but big speed
- Momentum is conserved
- So alpha has more energy, since is has small mass (Ek = p^2/2m)
三、宇宙的膨胀
如果宇宙中没有暗物质会怎么样
- Dark matter adds mass to universe, and it increases the average density of the universe.
- Reduce the density of the universe.
- The ultimate fate of the universe is dependent upon the average density.
- If the density of the universe is less than a critical value, the the universe may continue to expand forever.
暗物质是什么(2016.5)
- Cannot be detected via em-interaction
- It has mass (it exerts gravitational force)
解释多普勒效应对波长的影响
- There is a Doppler shift.
- Motion towards the observer decreases the wavelength detected.
- The hydrogen atoms have a range of velocities hence there is a range of wavelengths detected
解释red shift
Red shift is the fractional increase in the wavelength received. Due to the source of radiation moving away from the observer.
四、宇宙的演变
低质量到中等质量恒星(例如太阳)的演化过程
- When hydrogen fusion ends main sequence stars evolve into red giant stars.
- This happens first for stars near the top of the main sequence.
- Red giant stars are located above the main sequence.
- When helium fusion ends red giant stars evolve into white dwarf stars. White dwarf stars are located below the main sequence.
- Red giant stars are larger in surface area and have a lower surface temperature
为什么低质量的行星在main sequence比太阳时间更长
- 引力小,温度小–>核聚变的速率小
- Smaller gravitational force acting on it. (受到的力更小)
- The temperature in the core of
would be less. (温度更小) would have a lower rate of fusion, hence would exhaust its hydrogen more slowly. (核聚变的速率更小)
从HR diagram中如何得到星团的年龄
- Stars begin their life on the main sequence and evolve into red giant stars.
- Red giant stars then evolve into white dwarf stars.
- If the stars are mainly on the main sequence, as in Y, the star cluster is young.
- If there are red giant stars, as in Z, the star cluster is older.
- If there are white dwarf stars, as in X, the star cluster is the oldest.
五、简谐运动
Resonance发生的原因
- The frequency of the driving force is same as the natural frequency.
- There is a maximum transfer of energy
- Amplitude increases
Damping发生的原因
- Damping dissipate energy to the surroundings
- Amplitude decreases
某个绳子运动为什么是简谐运动(2016.5)
- It obeys Hooke’s law
六、Gravitational Field
地球同步卫星和低轨卫星的区别(2016.1)
- Orbit must be higher
- Has an orbital time of 24 hours
- The orbit must be in a equatorial plane
怎么看出来上图的B是来自太阳的辐射
Peak wavelength is in the middle of the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum(峰值波长处于电磁波谱的可见光区域的中间位置)
怎么看出来上图的A是来自一个更高表面温度的行星的辐射
$\lambda_{max}$ is small(最大波长最小)
解释A和B有什么不同
- The star emit more blue radiation (蓝移)
- The area under the graph is larger, so it has greater power output (功率输出更大)
为什么从太空到地面,重力场可以看作是均匀的(2014)
- 跳落的高度比地球的半径小的多
- g是基本不变的
本文使用CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 协议进行许可,如需转载必须署名https://blog.carkree.com ,不得进行任何的二次分发、演绎、修改(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/deed.zh-hans )